
ESWT - Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for ed
Available at StanTop Urology Clinic in Gangnam, Seoul, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a revolutionary treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED) that goes beyond achieving a single erection. Its goal is to restore the patient’s ability to achieve an erection naturally by applying low-intensity shock waves to the subcutaneous tissues of the penis, promoting the regeneration of blood vessels, muscles, and erectile tissue in the penis.
Who is ESWT suitable for?

- Men who are dissatisfied with their erectile function
- Middle-aged and older men lose self-confidence due to erectile problems.
- Those who have tried various methods without successThose who have tried various methods without success
- Men who feel their penis size is insufficient
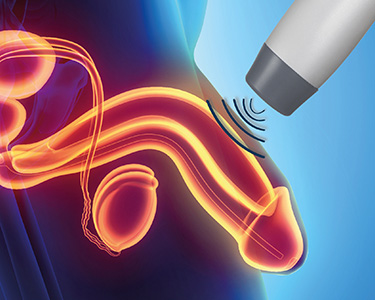
Advantages of ESWT
- Without drugs, surgeries, hospitalization and scars
- Painless treatment aimed at eliminating the underlying cause
- Non-invasive therapy that allows immediate return to daily activities.
- Restoring natural erectile function
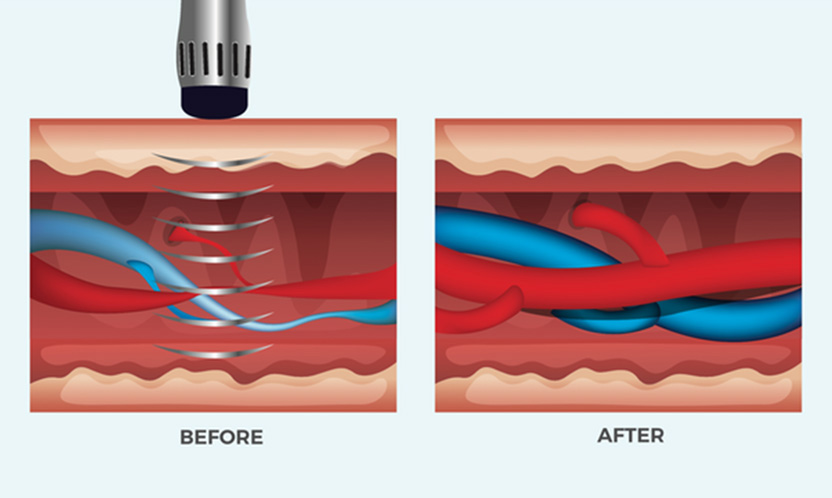
Aging and cardiovascular problems can impair the vascular function of the subcutaneous tissue of the penis, resulting in insufficient blood flow during erection and difficulty achieving a natural erection.
The use of low-intensity shock waves promotes the formation and expansion of new blood vessels, as well as improving the function of surrounding tissues. This restores blood flow to the subcutaneous tissue of the penis, providing a natural erection.
Types of Three-Piece Penile Prostheses

ED1000
An ESWT device that delivers shock waves directly to the penile tissue, stimulating the regeneration of blood vessels, muscles, nerves and other erectile tissue. It is a pioneering treatment approved by the FDA/KFDA.

RENOVA
The first ESWT device with magnetic field introduced in South Korea by StanTop Urology Clinic. It offers a broader and deeper treatment spectrum, reducing the number of sessions and treatment time.

Indications
- Inability to achieve an erection even with spontaneous or sexual stimulation.
- Short-lived or flaccid erection before insertion.
- Insufficient rigidity during erection or inability to maintain rigidity during penetration.
- Achieving an erection but lacking the rigidity needed for successful intercourse.
- Decreased frequency of morning erections.
